Topical application of Hair Thickening Serum (HTS) promotes hair growth by two key means: Providing, 1. Skin and hair follicle endogenous molecules from skin and hair follicle stem cells (Adipose mesenchymal stem cells, fibroblasts, and dermal papillae) that drive and maintain the transition from telogen to anagen, and 2. Botanical ingredients normally derived from healthy diets that support hair growth.
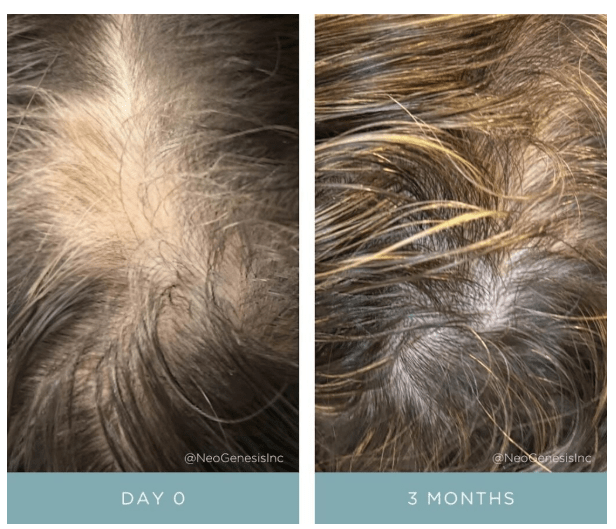
Simple topical application of NeoGenesis Hair Thickening Serum, b.i.d., twice daily.
Let’s look at the hair growth cycle, and some of the many factors affecting hair growth. I’ll then explain some the mechanisms by which HTS drives the hair follicle to the anagen phase.
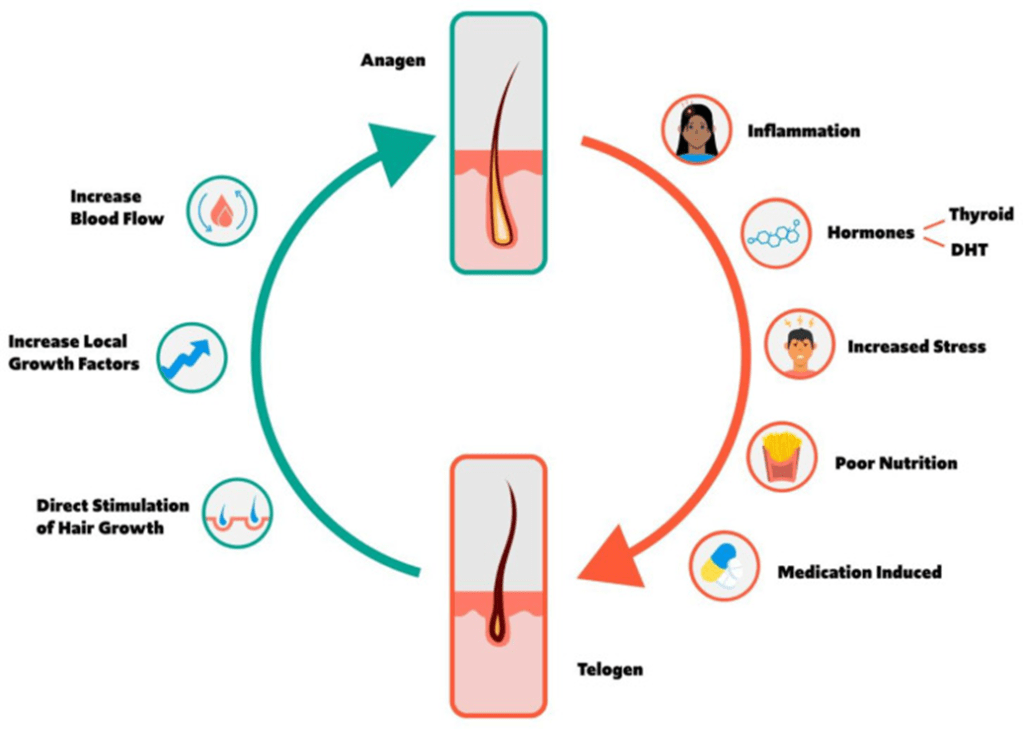
Figure 1. Schematic of the hair growth cycle and the factors that may influence a transition from anagen to telogen vs. telogen to anagen phase. From Natarelli et al, 2023.
HTS Mechanisms of Action in the Hair Growth Cycle
HTS’ mechanisms of action at the hair follicle are many. Here I consider a simplified summary of some of the pathways that the stem cell released molecules and botanical ingredients activate or inhibit to drive and maintain the follicle’s transition to the anagen phase.
Transition from Anagen to Telogen
Inflammation – An immunoprivileged state in the follicle is needed to drive anagen, and inflammation transitions the follicle to telogen instead (Bertolini et al, 2020). HTS reduces inflammation in the innate and adaptive immune systems by using the secretome from adipose mesenchymal stem cells – both the exosomal fraction and soluble fractions that act synergistically to optimally reduce inflammation (González-Cubero et al, 2022; Mitchell et al, 2019)
Hormone – ADSC secretome inhibits negative effects of DHT on hair growth (Tang et al, 2023; Fu et al, 2025).
Poor Nutrition – HTS contains nutrients to support hair growth. Larix Europaea Wood Extract, containing Dihydroquercetin-glucoside (polyphenol), EGCG (polyphenol catechin), glycine, zinc, Camellia Sinensis Leaf Extract, Santalum Acuminatum Fruit Extract, Citrus Glauca Fruit Extract, Acacia Victoriae Fruit Extract, Trifolium Pratense (Clover) Flower Extract (providing an abundance of polyphenols and antioxidants).
Stress – ADSC secretome mitigates immunological disturbances affecting the hair follicle (HF) and contributing to hair loss. ADSCs are able to suppress lymphocyte proliferation and, inhibit complement activation and dendritic cell differentiation from monocytes and therefore are considered natural immunosuppressants (Salhab et al, 2022).
Transition from Telogen to Anagen
Blood Flow – Secretome of ADSCs promotes angiogenesis and increased blood flow to follicles (Silveira et al, 2022; Zhu et al, 2020)
Direct stimulation of Hair Growth – Exosomes from dermal papillae cells drive hair follicle stem cell proliferation to rebuild hair follicle (Li et al, 2023), while fibroblasts provide many building-block proteins need to reconstruct the follicle architecture as it transitions from telogen to anagen (Suh et al, 2023).
Increased Local Growth factors – Fibroblasts (Lin et al, 2015), ADSCs (Won et al, 2017), and dermal papillae (HU et al, 2020) secretome all provide necessary growth factors to induce transition to anagen
References
Bertolini M et al (2020) Hair follicle immune privilege and its collapse in alopecia areata. Exp Dermatol. 29: 703–725.
Fu Y, Han YT, Xie JL, Liu RQ, Zhao B, Zhang XL, Zhang J, Zhang J. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance the development of hair follicle to ameliorate androgenetic alopecia. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(3): 102088
Fu Y, Han YT, Xie JL, Liu RQ, Zhao B, Zhang XL, Zhang J, Zhang J. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance the development of hair follicle to ameliorate androgenetic alopecia. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(3): 102088 [PMID: 40160691 DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.102088]
González-Cubero, E et al (2022) María L. González-Fernández, Elias R. Olivera, Vega Villar-Suárez,Extracellular vesicle and soluble fractions of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells secretome induce inflammatory cytokines modulation in an in vitro model of discogenic pain,The Spine Journal,Volume 22, Issue 7,2022, Pages 1222-1234
Li J, Zhao B, Yao S, Dai Y, Zhang X, Yang N, Bao Z, Cai J, Chen Y, Wu X. Dermal PapillaCell-Derived Exosomes Regulate Hair Follicle Stem Cell Proliferation via LEF1. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):3961.
Lin WH, Xiang LJ, Shi HX, Zhang J, Jiang LP, Cai PT, Lin ZL, Lin BB, Huang Y, Zhang HL, Fu XB, Guo DJ, Li XK, Wang XJ, Xiao J. Fibroblast growth factors stimulate hair growth through β-catenin and Shh expression in C57BL/6 mice. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:730139.
Mitchell R et al (2019) Secretome of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes skeletal muscle regeneration through synergistic action of extracellular vesicle cargo and soluble proteins. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10(1):116.
Natarelli N, Gahoonia N, Sivamani RK (2023) Integrative and Mechanistic Approach to the Hair Growth Cycle and Hair Loss. J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 23;12(3):893.
Salhab O, Khayat L, Alaaeddine N (2022) Stem cell secretome as a mechanism for restoring hair loss due to stress, particularly alopecia areata: narrative review. J Biomed Sci. 2022 Oct 5;29(1):77.
Shiqi Hu et al. (2020) Dermal exosomes containing miR-218-5p promote hair regeneration by regulating β-catenin signaling.Sci. Adv.6,eaba1685(2020).
Silveira BM, Ribeiro TO, Freitas RS, Carreira ACO, Gonçalves MS, Sogayar M, et al. (2022) Secretome from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes blood vessel formation and pericyte coverage in experimental skin repair. PLoS ONE 17(12): e0277863.
Suh SB, Ahn KJ, Kim EJ, Suh JY, Cho SB. (2023) Proteomic Identification and Quantification of Secretory Proteins in Human Dermal Fibroblast-Conditioned Medium for Wound Repair and Hair Regeneration. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:1145-1157
Tang, Xin, Cao, Cuixiang, Liang, Yunxiao, Han, Le, Tu, Bin, Yu, Miao, Wan, Miaojian, Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes Antagonize the Inhibitory Effect of Dihydrotestosterone on Hair Follicle Growth by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway, Stem Cells International, 2023, 5548112, 20 pages, 2023.
Won CH et al (2017) The Basic Mechanism of Hair Growth Stimulation by Adipose-derived Stem Cells and Their Secretory Factors. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(7):535-543
Zhu, D., Johnson, T.K., Wang, Y. et al. (2020) Macrophage M2 polarization induced by exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells contributes to the exosomal proangiogenic effect on mouse ischemic hindlimb. Stem Cell Res Ther 11, 162.