Despite the years of research on the ill effects of SLS (sodium lauryl sulfate), I continue to hear that people, including dermatologists, are using products with this ingredient, including shampoos.
If you’ve ever Googled the causes of a skin irritation or damaged hair, you’ve likely seen posts about SLS, or sodium lauryl (or laureth) sulfate, a common ingredient in beauty products, cleansers, shampoos, toothpastes, and cleaning products.
So what does this ingredient do, why is it in everything, and what does the evidence say about how safe it is?
When we use a cleanser or shampoo, the product usually contains a detergent. That detergent is called a surfactant. A surfactant allows the oil and water molecules to bind together – it’s what’s found in soaps and detergents so we can wash our oily faces or dishes with water and remove the grime.
Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) is a surfactant, and its efficacy, low cost, abundance and simplicity mean it’s used in a variety of cosmetic, dermatological, and consumer products.
Our skin’s outermost layer, the stratum corneum of the epidermis, is specially designed to keep harmful things out, and this is where a surfactant can cause problems. Using chemicals that weaken this barrier defence mechanism can potentially cause our skin harm.
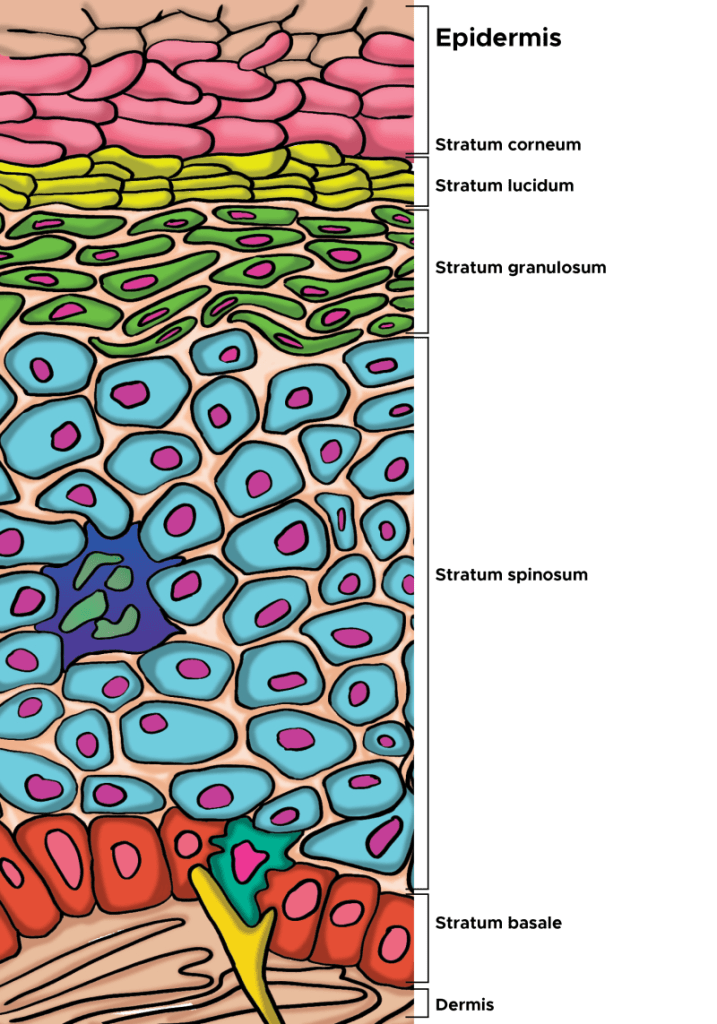
As the outermost layer of the epidermis, the stratum corneum is the first line of defense for the body, serving an essential role as a protective skin barrier against the external environment. The stratum corneum aids in hydration and water retention, which prevents skin cracking, and is made up of corneocytes, which are anucleated keratinocytes that have reached the final stage of keratinocyte differentiation (From Murphrey et al, 2022).
Some surfactants are more irritating to our skin than others. For something to be harmful, irritating or allergenic, it has to fulfill two criteria. It has to have been found in studies to irritate human skin, and it has to have the ability to penetrate the skin. SLS does both. It penetrates the stratum corneum and induces an immune reaction, and degrades the structure of the barrier.
Scientists in Germany tested 1,600 patients for SLS irritancy and found 42% of the patients tested had an irritant reaction. Another study, on seven volunteers over a three and a half month period, found regular contact caused irritation, and the irritation subsided once the skin was no longer exposed to SLS. Another study found the warmer the water used with SLS, the more irritating it will be.
SLS is a well established irritatant and is used as a positive control in dermatological testing. That is, new products being tested to see how irritating they might be to human skin are compared to the known irritant, SLS. If a person is sensitive to SLS, they might find the area that has been in contact is red, dry, scaly, itchy or sore. It’s also important to note there’s no scientific evidence SLS causes cancer, despite what is often posted on the internet. So, it’s probably OK to use SLS in products that are used for household cleaners.
Who should avoid SLS?
Everyone, especially people with a history of sensitive skin, hyperirritable skin and patients suffering from skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis (eczema), rosacea, and psoriasis are best to avoid products containing SLS. If you think it might be SLS causing a skin irritation, stop the use of the product and look for products that don’t contain SLS.